Betsy Arakawa, the wife of acclaimed actor Gene Hackman, has died due to complications from a rare respiratory illness associated with hantavirus. This disease, primarily transmitted through contact with infected rodents, can lead to serious health issues, specifically Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS). Health officials noted that Ms. Arakawa's death is linked to HPS, which she is believed to have contracted from environment exposure.
Authorities discovered the couple in their New Mexico home following her passing, which occurred shortly before her husband, who suffers from advanced Alzheimer's disease.
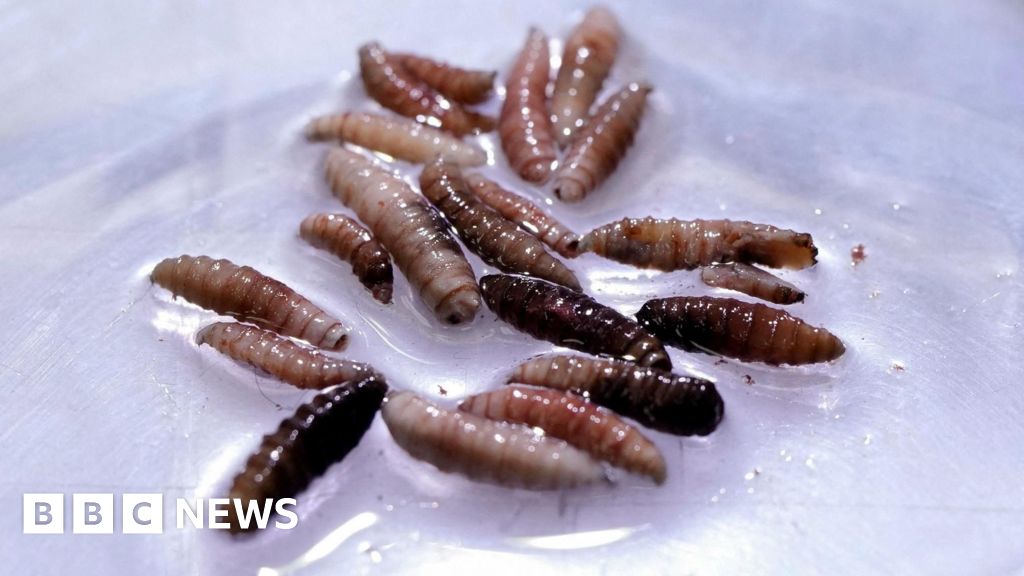
What is hantavirus? It's a viral strain associated with rodents, predominantly transmitted to humans via inhalation of airborne particles from dried droppings. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) asserts that infections can arise when rodent urine, droppings, or saliva become airborne, and on rare occasions, through bites or scratches from infested rodents, particularly deer mice in North America.
There are two critical health conditions linked to hantavirus: the aforementioned Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome, which is the predominant strain in the U.S., and Haemorrhagic Fever with Renal syndrome, which impacts kidney functionality.
Initial symptoms of HPS include fatigue, fever, muscle aches, followed by headaches and respiratory issues. The CDC reports a mortality rate near 38% if respiratory symptoms arise.
From 1993 to 2022, the CDC documented 864 hantavirus cases across the U.S., mostly located in rural western states. Surveillance for the disease began in 1993 following a spike in severe respiratory ailments in the Four Corners region, including Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah. On a global scale, Haemorrhagic Fever with Renal syndrome reportedly afflicts approximately 150,000 people annually, with the majority of cases occurring in China.
Treatment for hantavirus is limited; there is no specific cure. Patients are encouraged to receive supportive care to alleviate symptoms, and those presenting severe manifestations may require hospitalization and potential intubation. Preventative measures include minimizing rodent contact in living or work environments, sealing entry points in homes, and using protective gear when handling rodent waste.