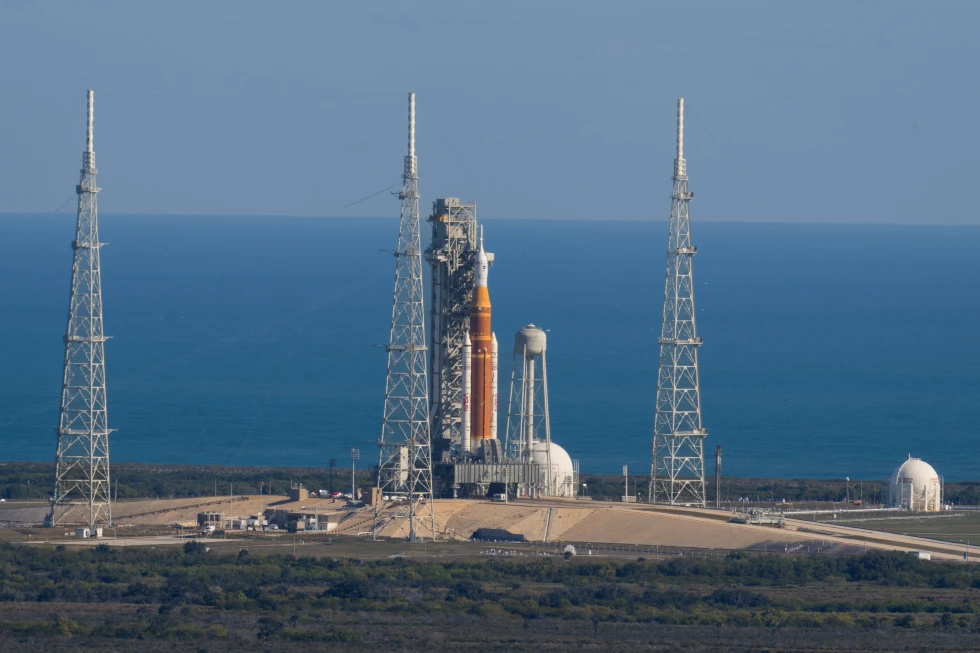
As NASA submits its budget request to Congress, it faces potential funding reductions of nearly half, which would halt 40 science missions already in development or active in space. Central to the conflict is the reliance of NASA on Musk's SpaceX for critical operations such as supplying the International Space Station with crew and materials through the Falcon 9 rocket fleet. Furthermore, the emerging Starship rocket, pivotal for lunar and Martian missions, remains under development.
Dr. Simeon Barber, a space scientist, criticized the disruptive impacts of recent political exchanges, noting that such conditions undermine long-term planning and task cooperation between governmental agencies, businesses, and academia. While the proposed budget cuts apply generally, an exception exists for the Mars mission, which has seen a modest increase in funding.
Experts like Casey Dreier from the Planetary Society label these potential cuts as the "biggest crisis ever" to the U.S. space program, emphasizing that the proposal to cut overall NASA funding by nearly 25% aligns with shifting priorities towards lunar and Martian exploration. Dr. Adam Baker of Cranfield University warned that if these proposals receive congressional approval, it would fundamentally reshape NASA’s objectives and capabilities.
Supporters of the budget cuts argue that a streamlined focus could provide NASA with clear operational goals reminiscent of the Apollo-era missions. Critics contend that considerable waste and inefficiency has beset the agency over the years, illustrated by the exorbitant costs associated with its Space Launch System (SLS).
Under the proposed cuts, NASA may phase out SLS in favor of commercially developed alternatives like SpaceX's Starship or Blue Origin's New Glenn. However, uncertainties abound regarding these alternatives' reliability and developmental readiness.
Concerns mount as 40 vital projects—including planetary missions and climate monitoring—could face termination. Collaborations with international partners, such as the European Space Agency's Mars initiatives, may also be jeopardized, leading to diminished global space exploration efforts.
Despite these challenges, some European leaders see an opportunity to enhance their autonomous capabilities in space exploration, but the short-term implications could be detrimental. Cuts could affect access to shared facilities like the International Space Station and undermine contributions to future multinational projects like the Lunar Gateway.
As debate rages over potential budget proposals, lobbyists note a divide among lawmakers, with many Republicans expressing reluctance to support the cuts. The looming political stalemate poses a risk of no fiscal agreement, resulting in interim budget measures that could prove difficult to reverse.
If approved, these funding reductions might set a precarious precedent, leading to irreversible impacts on ongoing and future space missions, prompting widespread concerns over the trajectory of U.S. space exploration.
Dr. Simeon Barber, a space scientist, criticized the disruptive impacts of recent political exchanges, noting that such conditions undermine long-term planning and task cooperation between governmental agencies, businesses, and academia. While the proposed budget cuts apply generally, an exception exists for the Mars mission, which has seen a modest increase in funding.
Experts like Casey Dreier from the Planetary Society label these potential cuts as the "biggest crisis ever" to the U.S. space program, emphasizing that the proposal to cut overall NASA funding by nearly 25% aligns with shifting priorities towards lunar and Martian exploration. Dr. Adam Baker of Cranfield University warned that if these proposals receive congressional approval, it would fundamentally reshape NASA’s objectives and capabilities.
Supporters of the budget cuts argue that a streamlined focus could provide NASA with clear operational goals reminiscent of the Apollo-era missions. Critics contend that considerable waste and inefficiency has beset the agency over the years, illustrated by the exorbitant costs associated with its Space Launch System (SLS).
Under the proposed cuts, NASA may phase out SLS in favor of commercially developed alternatives like SpaceX's Starship or Blue Origin's New Glenn. However, uncertainties abound regarding these alternatives' reliability and developmental readiness.
Concerns mount as 40 vital projects—including planetary missions and climate monitoring—could face termination. Collaborations with international partners, such as the European Space Agency's Mars initiatives, may also be jeopardized, leading to diminished global space exploration efforts.
Despite these challenges, some European leaders see an opportunity to enhance their autonomous capabilities in space exploration, but the short-term implications could be detrimental. Cuts could affect access to shared facilities like the International Space Station and undermine contributions to future multinational projects like the Lunar Gateway.
As debate rages over potential budget proposals, lobbyists note a divide among lawmakers, with many Republicans expressing reluctance to support the cuts. The looming political stalemate poses a risk of no fiscal agreement, resulting in interim budget measures that could prove difficult to reverse.
If approved, these funding reductions might set a precarious precedent, leading to irreversible impacts on ongoing and future space missions, prompting widespread concerns over the trajectory of U.S. space exploration.